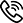In the suspension system, because elastic elements are impacted to cause
vibration, the shock absorber and elastic elements are installed in
parallel in the suspension in order to improve driving smoothness of
automobiles; in order to reduce vibration, the shock absorbers widely
used in the automotive suspension system are often hydraulic shock
absorbers, its working principle is that: when the relative motion
between the automobile frame (or automobile body) and the driving axle
occurs due to vibration, the piston in the shock absorber moves up and
down, the oil in the cavities of the shock absorber repeatedly flows
from one cavity to another cavity via different holes, at this time, the
friction between the hole walls and the oil and between oil molecules
form the damping force, and the vibration energy of the automobile is
converted into heat energy of the oil and then absorbed by the shock
absorber and emitted to the atmosphere. Under the condition of the same
total sectional area of oil channels, the damping force of the shock
absorber increases or decreases along with the increase or decrease of
the relative motion speed of the automobile frame and the driving
axle(or wheels), and is related to viscosity of the oil. The shock
absorber and the elastic elements take the task of buffering impact and
reducing vibration. When the damping force is too big, the elasticity of
the suspension will get bad, even the connecting piece of the shock
absorber is damaged, so that the contradiction between the elastic
elements and the shock absorber must be solved.
(1) In the
compression stroke (the driving axle and the automobile frame are
closing to each other), the damping force of the shock absorber is small
so as to give a full play of the elastic action of elastic elements to
buffer impact. At this time, the elastic elements play a leading role;
(2)In
the stretching stroke (the driving axle and the automobile frame are
getting away from each other), the damping force of the shock absorber
should be big, so that the vibration can be reduced quickly;
(3)When
the relative speed between the driving axle (or wheels) and driving axle
is too high, the shock absorber should automatically increase the flow
rate of the oil, so that the damping force is kept in a certain range so
as to avoid too big impact load;
The telescopic shock absorber is
widely used in the automotive suspension system, and the shock absorber
which has the shock absorbing effect in both compression stroke and
stretching stroke is the bi-directional action type shock absorber; in
addition, some new shock absorbers including gas filling type shock
absorbers and damping force adjusting shock absorbers are also used.
The
working principle of the bi-directional action telescopic shock
absorber is that: in the compression stroke, namely the automobile
wheels move close to the automobile body, the shock absorber is
compressed, the piston 3 of the shock absorber moves downward, the
volume of the lower cavity of the piston is decreased, the oil pressure
rises, the oil flows to the cavity (upper cavity) above the piston via
the passing valve 8, and the partial space of the upper cavity is
occupied by the piston rod 1, so that the increased volume of the upper
cavity is less than the decreased volume of the lower cavity, some oil
pushes the compression valve 6 and flows back to the oil cylinder 5, and
the oil-saving action of these valves forms the damping force against
the compressed motion of the suspension; in the stretching stroke of the
shock absorber, the wheels are relatively away from the automobile
body, the shock absorber is stretched, the piston of the shock absorber
moves upward, the oil pressure of the lower cavity of the piston rises,
the passing valve 8 is closed, the oil in the upper cavity pushes the
stretching valve 4 and flows to the lower cavity; and because of the
existence of the piston rod, the oil flowing from the upper cavity is
not enough to fill up the increased space of the lower cavity, so that a
certain vacuum degree is generated in the lower cavity, the oil in the
oil storage cylinder pushes the compensation valve 7 and flows to the
lower cavity for supplement, and the throttling action of these valves
forms the damping force against the stretching motion of the suspension.
Because
the designed rigidity and pre-tightening force of the stretching valve
are greater than those of the compression valve, under the same
pressure, the total sectional area of the stretching valve and the
channels of the corresponding normal open gaps is less than that of the
compression valve and the channels of the corresponding normal open
gaps, so that the damping force generated in the stretching stroke of
the shock absorber is more than that generated in the compression stroke
of the shock absorber, and the aim of quickly reduce the vibration is
achieved.
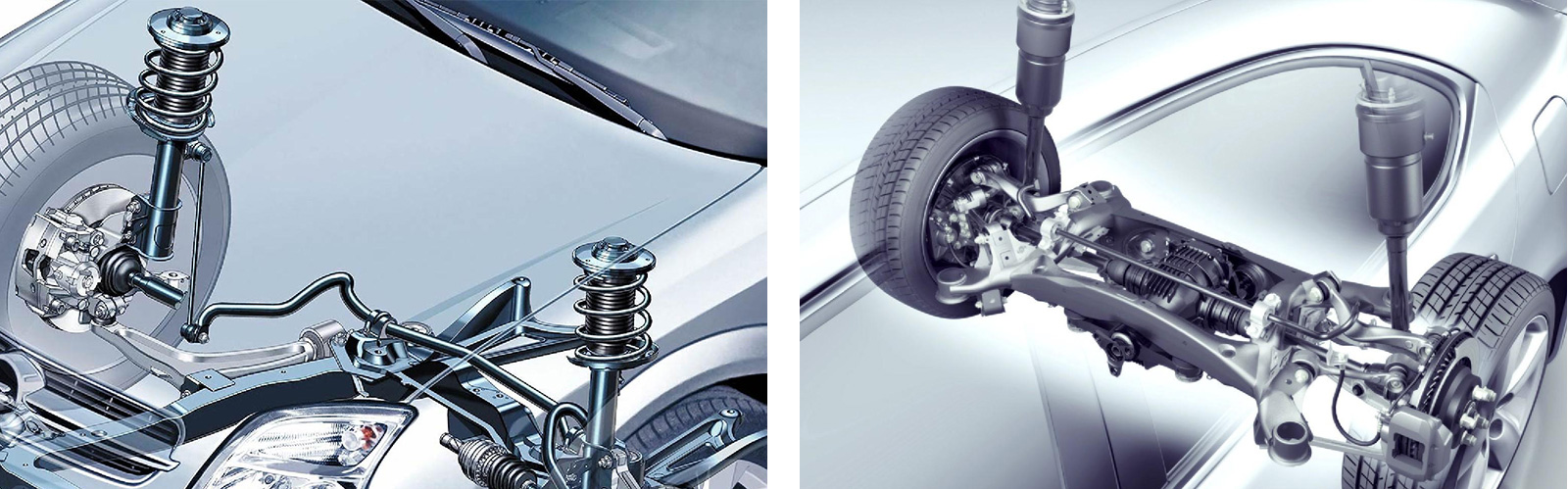
The following drawing shows the structural drawing of front
and rear suspension shock absorbers of an automobile. Its working
principle has been introduced above.
- Products
-
- -Air Suspension Strut
- -Electronic Shock Absorber
- -Electronic Air Suspension
- -Cartidge shock absorber
- -Monotube shock absorber
- -Double-tube shock absorber
- -Modified car shock absorber
- -Assembly shock absorber
- -Truck shock absorber
- -Steer damper
- -Golf car shock absorber
- -Suspension Coil Spring
- -Lifted or Lowering Spring
Yangzhou Focus Shock Absorber Co., Ltd.
Technological leadership and innovative quality improvement
Yangzhou Focus Shock Absorber Co., Ltd.
Technological leadership and innovative quality improvement
Yangzhou Focus Shock Absorber Co., Ltd.
Technological leadership and innovative quality improvement